NavyWatch Blog – UK
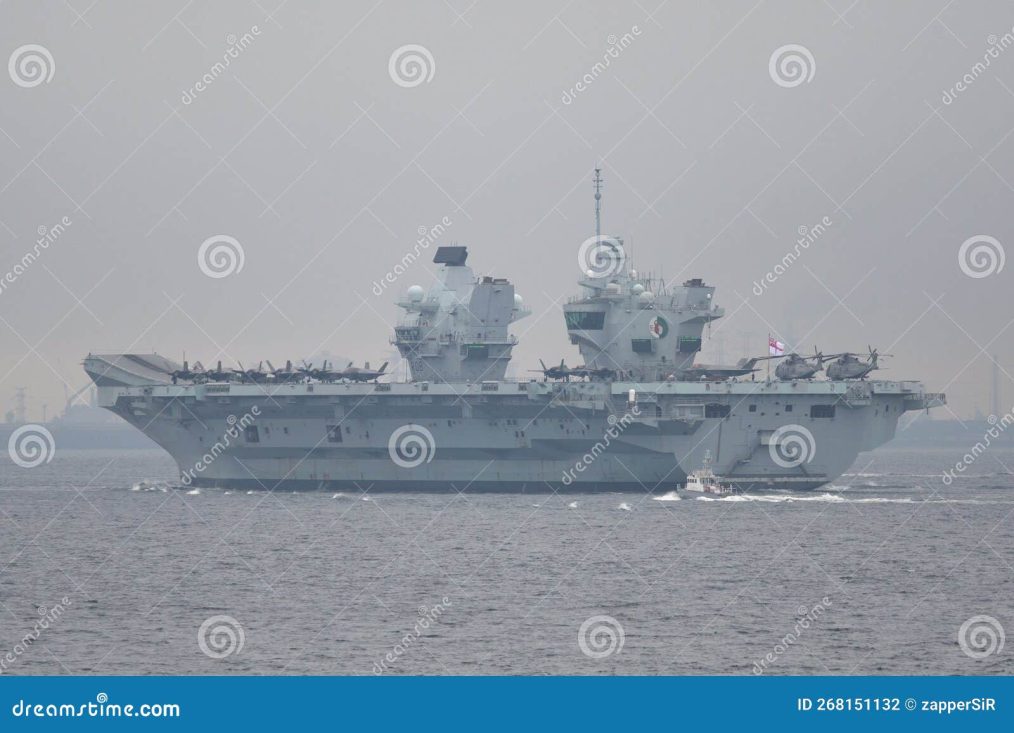
In February 2024, mechanical issues with the propulsion system of a major naval aircraft carrier forced it to withdraw from an important NATO exercise. This was one in a series of technical problems affecting the latest class of British carriers, raising concerns about their reliability and operational readiness.
The issue was detected during routine pre-sailing checks, revealing a problem with a coupling on the starboard propeller shaft. As a result, the vessel remained in port and was unable to join Exercise Steadfast Defender, the largest NATO maritime drill since the Cold War. The carrier was scheduled to operate alongside its sister ship, which had recently returned to service after experiencing similar propulsion failures.
Recurring issues with propulsion systems have led to questions about whether these mechanical failures are typical of new warship designs or indicative of deeper systemic flaws. While minor defects often emerge as ships undergo real-world operations, the frequency and severity of these problems suggest potential design shortcomings.
A similar vessel suffered a breakdown in 2022, just a day after departing for a U.S. deployment. The cause was traced to a misaligned propeller shaft, prompting thorough inspections of the other carrier in the class. Engineers reported no misalignment issues, and officials deemed the problems unrelated to a broader design flaw. However, recurring malfunctions continue to disrupt operations, prompting scrutiny of the fleet’s engineering integrity.
By contrast, other nations’ carriers have faced fewer propulsion-related difficulties. France’s sole nuclear-powered carrier, commissioned in 2001, has seen limited breakdowns, while the U.S. Navy’s newest carrier resolved its propulsion issues early without long-term setbacks.
As these challenges persist, the question remains: are these growing pains of a new fleet, or signs of a larger problem?